Mortgages!

Mortgages
A mortgage is a loan secured by property, usually real estate property. Lenders define it as the money borrowed to pay for real estate. In essence, the lender helps the buyer pay the seller of a house, and the buyer agrees to repay the money borrowed over a period of time, usually 15 or 30 years in the U.S. Each month, a payment is made from buyer to lender. A portion of the monthly payment is called the principal, which is the original amount borrowed. The other portion is the interest, which is the cost paid to the lender for using the money. There may be an escrow account involved to cover the cost of property taxes and insurance. The buyer cannot be considered the full owner of the mortgaged property until the last monthly payment is made. In the U.S., the most common mortgage loan is the conventional 30-year fixed-interest loan, which represents 70% to 90% of all mortgages. Mortgages are how most people are able to own homes in the U.S.
wHAT IS THE Mortgage Calculator?
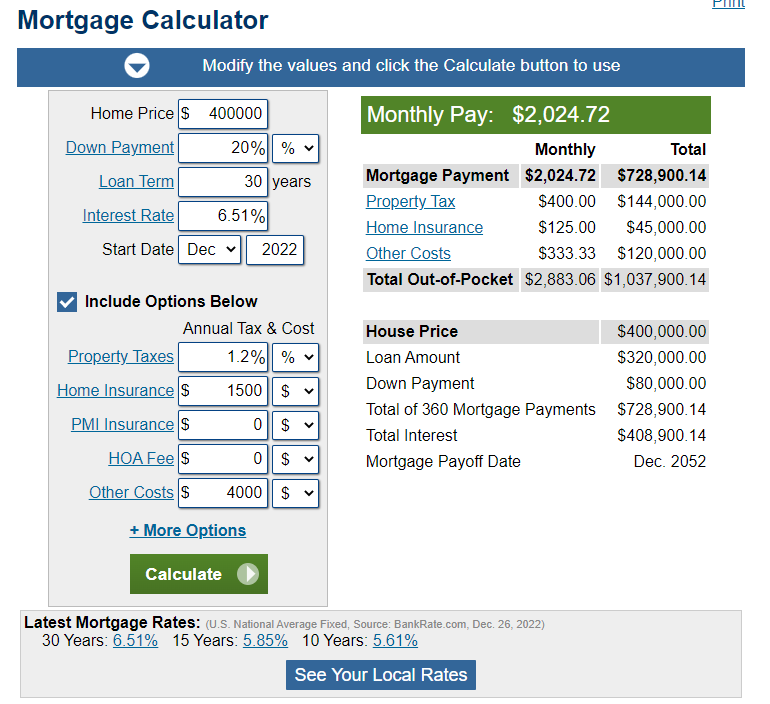
The Mortgage Calculator helps estimate the monthly payment due along with other financial costs associated with mortgages. There are options to include extra payments or annual percentage increases of common mortgage-related expenses. The calculator is mainly intended for use by U.S. residents.
Mortgage Calculator Components
A mortgage usually includes the following key components. These are also the basic components of a mortgage calculator.
Loan amount—the amount borrowed from a lender or bank. In a mortgage, this amounts to the purchase price minus any down payment. The maximum loan amount one can borrow normally correlates with household income or affordability. To estimate an affordable amount, please use our House Affordability Calculator.
Down payment—the upfront payment of the purchase, usually a percentage of the total price. This is the portion of the purchase price covered by the borrower. Typically, mortgage lenders want the borrower to put 20% or more as a down payment. In some cases, borrowers may put down as low as 3%. If the borrowers make a down payment of less than 20%, they will be required to pay private mortgage insurance (PMI). Borrowers need to hold this insurance until the loan's remaining principal dropped below 80% of the home's original purchase price. A general rule-of-thumb is that the higher the down payment, the more favorable the interest rate and the more likely the loan will be approved.
Loan term—the amount of time over which the loan must be repaid in full. Most fixed-rate mortgages are for 15, 20, or 30-year terms. A shorter period, such as 15 or 20 years, typically includes a lower interest rate.
Interest rate—the percentage of the loan charged as a cost of borrowing. Mortgages can charge either fixed-rate mortgages (FRM) or adjustable-rate mortgages (ARM). As the name implies, interest rates remain the same for the term of the FRM loan. The calculator above calculates fixed rates only. For ARMs, interest rates are generally fixed for a period of time, after which they will be periodically adjusted based on market indices. ARMs transfer part of the risk to borrowers. Therefore, the initial interest rates are normally 0.5% to 2% lower than FRM with the same loan term. Mortgage interest rates are normally expressed in Annual Percentage Rate (APR), sometimes called nominal APR or effective APR. It is the interest rate expressed as a periodic rate multiplied by the number of compounding periods in a year. For example, if a mortgage rate is 6% APR, it means the borrower will have to pay 6% divided by twelve, which comes out to 0.5% in interest every month.